Weight loss is a journey that numerous people undertake, but the road to achieving that desired figure can be winding and fraught with misinformation. To establish a realistic and sustainable weight loss regimen, it’s essential to comprehend the fundamental science behind weight loss, different diet types, and the vital role of exercise. This article aims to provide an in-depth explanation of these concepts to aid in your weight loss journey.
Calorie Deficit: The Bedrock of Weight Loss
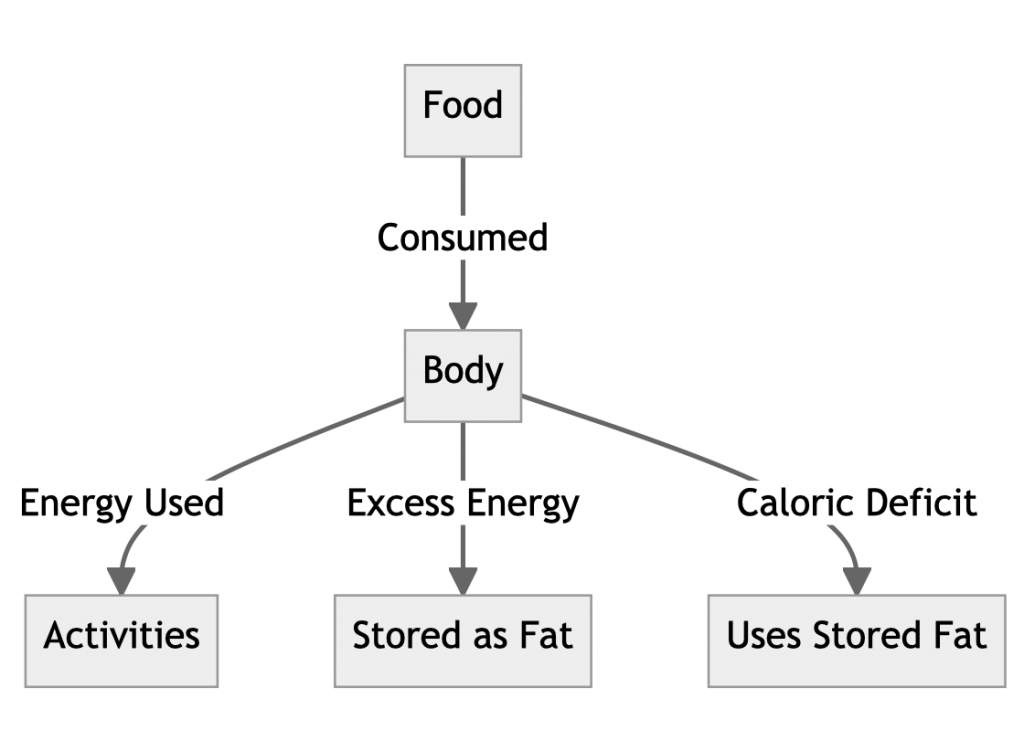
In simple terms, weight loss occurs when the body burns more calories than it consumes – a state known as a caloric deficit. Your body requires energy to function, and it sources this energy from the food you eat.
When you consume food, your body uses these calories to perform various functions such as breathing, circulating blood, adjusting hormone levels, and growing and repairing cells.
We refer to the energy unit in food as a calorie. When you consume fewer calories than your body needs for its daily activities, it resorts to burning stored fat for energy, leading to weight loss.
Metabolism: The Energy Manager
Metabolism refers to the biological process by which your body converts the food you eat into energy. It plays an important role in weight loss because it determines how many calories your body needs at rest (known as your basal metabolic rate). Several factors influence metabolism, including age, sex, muscle mass, physical activity, and certain medical conditions.
Many people perceive a “slow metabolism” as a hindrance to weight loss, but it’s worth noting that you can positively influence your metabolism, a dynamic process. Building muscle mass through resistance training and eating a balanced diet rich in protein can help boost your metabolic rate.
It is also important to note that Thyroid issues can have a significant impact on metabolism and weight loss due to the crucial role the thyroid gland plays in regulating metabolism.
If you suspect you have thyroid issues or are experiencing difficulties with weight management, we recommend consulting with your doctor for a proper diagnosis and guidance on appropriate treatment options.
Diet Types: A Look at the Menu
There’s no one-size-fits-all when it comes to diets for weight loss. Here are some of the most popular ones:
- Low-Carb Diets (e.g., Keto, Atkins): These diets limit the consumption of carbohydrates, driving the body into a state of ketosis where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbs.
- Low-Fat Diets: As the name suggests, these diets restrict fat intake, emphasizing foods high in protein and carbohydrates.
- Plant-Based Diets (e.g., Vegetarian, Vegan): These diets eliminate or drastically reduce the consumption of animal products, focusing more on plant foods.
- Intermittent Fasting: This eating pattern alternates between periods of eating and fasting.
While each diet has its merits, it’s crucial to find a diet that aligns with your lifestyle and health needs. Consulting with a dietitian or healthcare professional can help tailor a diet to your specific requirements. Learning to meal prep will also make this journey easier to stick to, especially for the busy bodies.
Exploring More Diet Types: A Diverse Palette of Weight Loss Options
- Paleolithic (Paleo) Diet: This diet bases its principles on the consumption of foods similar to those eaten during the Paleolithic era, such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while it advises limiting intake of processed foods, grains, and dairy.
- Mediterranean Diet: Inspired by the eating habits of Greece, Italy, and other Mediterranean countries, this diet emphasizes consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, nuts, legumes, olive oil, and flavorful herbs and spices. You should consume fish and seafood a couple of times a week, eat poultry, eggs, cheese, and yogurt in moderation, and limit your intake of red meat.
- DASH Diet:DASH, an acronym for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, is a diet that health professionals often recommend for lowering blood pressure. This diet promotes consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy, while limiting foods high in saturated fats and sugar.
- Flexitarian Diet: This diet is a flexible approach to a vegetarian diet. The followers of this diet primarily eat plant-based foods but can occasionally include meat or fish.
- Volumetrics Diet: Developed by nutritionist Barbara Rolls, the Volumetrics diet is about eating foods that make you feel full and satisfied, focusing on the energy density of foods.We encourage the consumption of high-volume, low-calorie foods like fruits and vegetables, while limiting the intake of high-calorie, low-volume foods.
- The Zone Diet: This diet, developed by biochemist Barry Sears, promotes a balanced ratio of carbohydrates (40%), fat (30%), and protein (30%) at each meal to reduce inflammation and increase satiety.
- The Macrobiotic Diet: This diet, rooted in Zen Buddhism, aims at balancing yin and yang elements of food and lifestyle.This diet emphasizes locally grown, organic vegetarian foods, whole grains, and fermented soy, while excluding processed foods and most animal products.

Sustainable Weight Loss Strategies
Sustainable weight loss isn’t about drastic short-term changes but rather developing long-term healthy habits. Here are some strategies:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity not only burns calories but also builds muscle, which can enhance your metabolic rate. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise each week.
We have training programs available here: Miami Fitness Training Programs - Mindful Eating: Pay attention to what and when you eat. This practice encourages an awareness of hunger and fullness cues, preventing overeating.
- Sleep Well: Lack of sleep can interfere with metabolism and appetite regulation, leading to weight gain. Prioritize quality sleep to support weight loss.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water can help manage hunger and maintain hydration, essential for general health and metabolism.
- Consistency: Losing weight takes time. Stay consistent with your healthy habits and remember that slow and steady often wins the race.
The Importance of Exercise

While diet primarily drives weight loss, exercise plays a significant role in maintaining weight loss and overall health. Regular physical activity helps build muscle mass, increases your metabolic rate, boosts mood, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
To conclude, understanding the science behind weight loss and implementing sustainable strategies can significantly improve the likelihood of long-term success. Remember that weight loss is a personal journey and what works for one might not work for another. Always consult with your healthcare professionals to ensure a safe and effective weight loss regimen tailored to your needs.


